
Designing products, spaces, and experiences has always been complex and evolving. Two terms that have gained significant traction in this context are accessibility and inclusive design. While both aim to improve things for everyone, the approach it different. This blog will reveal the secrets of accessible and inclusive design, their differences, and examples.
The choice between these designs for inclusivity will still depend on the context and objectives that a professional web design services company can work around and draw the best solution for your business. Before we decide which of these two approaches is best, let's know the differences between inclusive design vs accessibility.

Start Your Inclusive Design Journey
What is inclusive design? Let us now probe the accessibility vs inclusivity question for better clarity. Accessibility, by its dictionary definition, signifies something easy to reach, obtain, approach, or understand. In the web design context, accessibility primarily means that the design is perceivable, operable, and understandable to the broadest audience possible.
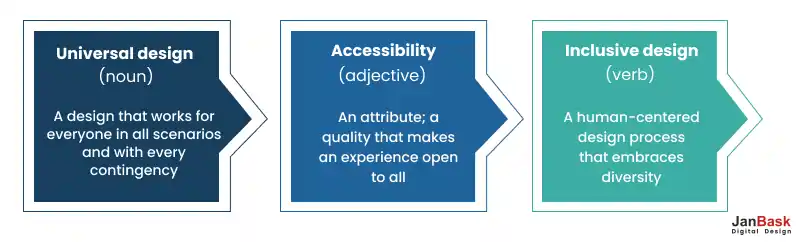
However, designing for accessibility extends beyond disability considerations; it involves diverse situations and contexts. True accessibility implies that a website should be usable by anyone, regardless of their limitations, whether temporary or permanent. It recognizes that users' circumstances can vary greatly, and a design that caters to this spectrum enhances the user experience for everyone.
Inclusive web design guides the creation of products, making them accessible to individuals from diverse backgrounds and with varying abilities. It breaks the boundaries of accessibility alone and uses various factors, including age, culture, economic circumstances, education, gender, geographic location, language, and race. The central goal is not merely to accommodate as many users as possible but to meet as many user needs as possible in which a professional web design service agency specializes.
A classic example of an inclusive web design is the MTA website that underwent a significant navigation overhaul to make it more user-friendly. Clear and consistent headings, menus, and links were implemented, making it easier for all users to find the information they need, including people using screen readers or keyboard navigation.
High Contrast and Color Choices: The website design includes a high-contrast color scheme, making it easier for users with low vision or color blindness to read and interact with the content. The color choices are carefully selected to ensure readability and legibility.
Want to get more details on accessible design vs. inclusive design? Check the next section.
Few important considerations involve inclusive design vs accessible design. Inclusive web design incorporates alt text for images. This text description not only assists users with visual impairments in understanding images but also benefits everyone when images don't load or in low-bandwidth situations. There are more such examples of this type of design. Let's explore them here:
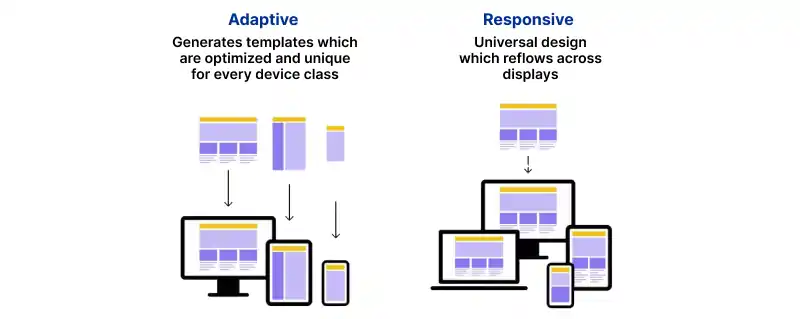
Websites with responsive design adapt to various screen sizes and devices. This inclusive approach ensures that users, whether on desktops, tablets, or smartphones.

You can use readable fonts and font sizes. This consideration aids users with visual impairments but also enhances the overall readability for all users, reducing eye strain.
When considering accessible design vs inclusive design, websites that prioritize keyboard navigation alongside mouse control are more inclusive. This benefits users with mobility challenges and those who prefer navigating without a mouse.

Providing captions for videos and transcripts for audio content is inclusive. It assists users with hearing impairments, but it's also valuable in noisy environments or when users want to scan content.
Between inclusive and accessible design, websites with inclusive forms provide clear error messages. This helps users with cognitive challenges or who must correct a mistake while filling out the form.
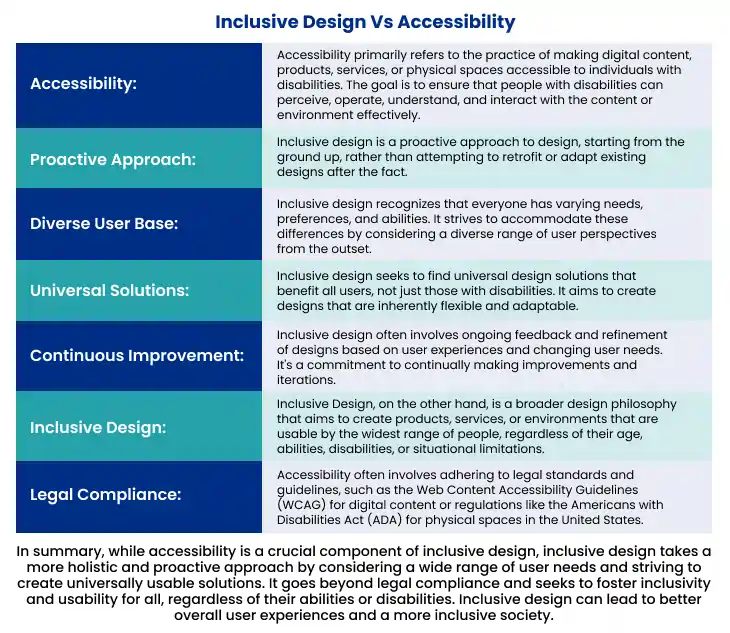
Within the context of accessible design vs inclusive design, inclusive web design isn't a one-size-fits-all approach. It prioritizes research and collaborative design processes, enabling a deeper understanding of your audience's needs. This understanding leads to more personalized solutions that can start by addressing the needs of a single individual but subsequently benefit many. Take a look at the numbers below

Users who perceive that your presence fulfills their specific requirements are likelier to engage with your content or products.
Successful brands that incorporate inclusive design often uncover new avenues for innovation. By considering the perspectives of marginalized groups, they create fresh styles, features, and options that cater to these users and attract a broader customer base. In doing so, they pioneer novel directions within their industries, setting trends that others follow.
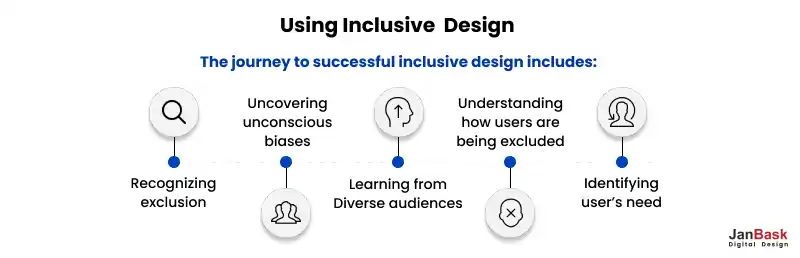
Many designers tend to fall into this trap of accessible design vs inclusive design, designing products based on their own preferences and behaviors. While you may be familiar with your creation, you must also recognize that your users will have different needs. So, which among the Inclusivity vs accessibility should you choose? Here are tips for inclusive design and why its above accessibility design.
Begin asking questions during the initial stages of the design process:
Often, designers unintentionally overlook alternative use cases because they rely on personal experiences and perspectives.
Identify the personas or user profiles you've envisioned when creating your design.
Alternative User Scenarios: Now, broaden your perspective and contemplate who else might use your product and under what circumstances. Think beyond the assumed user personas.
For instance, let's take the example of developing a mobile game. While audio content can impact the gaming experience, you must also provide alternative methods for accessing essential information that don't rely solely on listening. So, take scenarios where someone may have their volume down to avoid disturbing others or be in a noisy environment where audio cues are impractical.
Regular testing is an essential component of inclusive design as it helps identify and resolve your issues. The objective here is not to obtain a specific certification but to proactively address and rectify any obstacles within your product before they become ingrained.
Conducting WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) audits can also be useful in identifying barriers that may impact individuals with disabilities. Automated tests are another cost-effective option of identifying issues.
Color should not be the sole means of conveying information or instructions. For instance, instructing users to "click the green button" can confuse those with color vision deficiencies, low vision, or under bright lighting conditions. Instead, use clear and descriptive labels alongside colors.
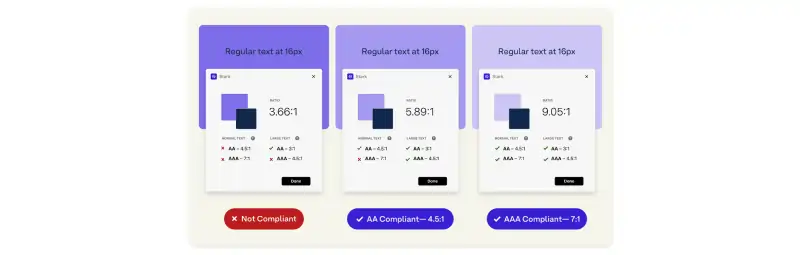
Pay close attention to color contrast ratios, as recommended by WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) Level AA. A minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1 for standard text and 3:1 for larger text (18 or 14 pt bold font) makes your content more readable against its background. Maintaining these ratios improves legibility for everyone.
Before incorporating colors into your design, you must conduct tests to evaluate their accessibility. Tools like the a11y® Color Contrast Accessibility Validator provide instant color contrast analysis.
A web designing services company like Janbask can be valuable in creating and maintaining your website, offering several practical ways to enhance your online presence.

A website designing services agency brings expertise and experience. They understand the nuances of effective web design, including layout, navigation, and user experience. Their insights can help you avoid common web design mistakes and make informed design decisions.
Web design partners work closely with you to understand your unique needs and goals. They can tailor the design to align with your brand identity and target audience, ensuring your website stands out and effectively communicates your message.
A reputable partner recognizes the importance of accessibility and inclusivity in web design. They can integrate best practices for making your website user-friendly for all, regardless of disabilities or limitations, helping you reach a broader audience.
With the increasing diversity of devices and screen sizes, responsive design is crucial. A professional web design service can make your website adapt to various devices for a user-friendly experience for all visitors.
Collaborating with a web design partner can expedite the design process. Their expertise allows for efficient project management, meeting deadlines, and reducing the time it takes to get your website up and running.
1. Why is accessible design different from inclusive design?
While both aim to enhance usability, accessible design accommodates specific disabilities, such as visual impairments or mobility limitations. In contrast, inclusive design takes a broader approach to create a more universally usable product.
2. How does inclusive design benefit from a holistic perspective?
Inclusive design thrives on a holistic perspective because it considers not only disabilities but also various identities, cultures, and perspectives. By embracing this holistic view, it fosters empathy and a deeper understanding of diverse user needs.
3. What's the key difference between accessibility and inclusivity regarding user engagement?
Accessible design primarily ensures that individuals with disabilities can engage with a product. Inclusive design, on the other hand, extends its reach to a broader audience.
4. Can accessible design be culturally specific or universally applicable?
Accessible design principles are intended to be universally applicable, focusing on accommodating disabilities rather than cultural differences. However, in practice, there can be instances where cultural context plays a role in accessibility considerations, such as language preferences or unique cultural usability needs.
5. Can inclusive design influence social change beyond digital interfaces?
Inclusive design can extend its influence beyond digital interfaces and contribute to broader social change. Promoting inclusivity and diversity in design can help challenge stereotypes.
The choice between inclusive design and accessibility, is not about selecting the "best" approach but recognizing the nature of these methodologies. JanBask's Website Design Services understands that both accessible and inclusive design serve essential purposes in improving your user experiences.
Rather than an either-or decision, Web Design Services at JanBask encourages a holistic approach that combines elements of both accessible and inclusive design. You also create a digital environment that adheres to accessibility standards.
Interested in our Web Design & Development Services?

J
It is one of the most informative blog clearing out the doubts and concepts.
Quite an interesting one.
A
Found this blog to be very useful.